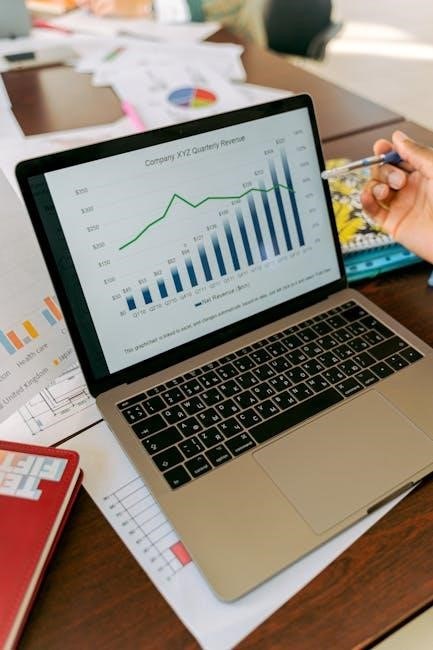
Financial accounting information provides a foundation for decision-making by offering insights into a company’s operational and financial performance․ It enables stakeholders to assess past activities, current financial status, and future prospects․ Reliable and relevant data are crucial for making informed decisions, ensuring transparency and accountability in business operations․ Understanding financial statements and their interrelationships is essential for effective decision-making processes․
1․1 Definition and Scope of Financial Accounting
Financial accounting is the process of identifying, measuring, and communicating economic information about an entity to stakeholders․ Its scope includes preparing financial statements like income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, ensuring transparency and accountability in business operations․ It provides essential data for assessing performance and making informed decisions․
1․2 Importance of Financial Accounting in Decision-Making
Financial accounting information is vital for decision-making as it provides insights into a company’s financial health․ Stakeholders use this data to evaluate performance, assess risks, and make informed choices․ By offering reliable and relevant information, financial accounting ensures transparency and accountability, enabling effective strategic planning and resource allocation for sustainable business growth and success․
Key Components of Financial Statements
Financial statements consist of three primary components: income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows․ These documents provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial position and performance․
2․1 Income Statement: Structure and Analysis
The income statement outlines revenues, expenses, and net income over a period․ It reveals profitability by subtracting costs from revenues․ Analysis involves identifying trends, margins, and expense ratios to assess performance and guide future decisions․ This statement is crucial for evaluating a company’s financial health and operational efficiency, aiding stakeholders in strategic planning and resource allocation․
2․2 Balance Sheet: Assets, Liabilities, and Equity
The balance sheet presents a company’s financial position at a specific point in time․ It categorizes assets, liabilities, and equity, providing insights into resource allocation and obligations․ Assets represent resources owned, liabilities are obligations due, and equity reflects ownership claims․ Analyzing the balance sheet helps assess solvency, liquidity, and investment potential, aiding stakeholders in making informed financial decisions․
2․3 Statement of Cash Flows: Sources and Uses of Funds
The statement of cash flows details cash inflows and outflows across operating, investing, and financing activities․ It reveals how a company generates and utilizes funds, indicating liquidity and solvency․ By analyzing cash flow patterns, stakeholders can assess financial stability, investment potential, and operational efficiency, aiding in strategic decision-making and resource management․
Role of Financial Statements in Decision-Making
Financial statements are crucial for decision-making, providing insights into past performance and future planning․ They ensure transparency and accountability, enabling stakeholders to make informed choices effectively․
3․1 Assessing Profitability and Financial Performance
Financial statements are crucial for assessing profitability and financial performance, providing insights into revenue growth, cost management, and net income trends․ Key metrics such as Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE) help evaluate operational efficiency and profitability․ These analyses inform strategic decisions, ensuring resources are allocated effectively for sustainable growth․
3․2 Evaluating Liquidity and Solvency
Liquidity and solvency are critical factors in assessing a company’s financial health․ Liquidity ratios, such as the current ratio, measure short-term debt repayment capacity, while solvency ratios, like the debt-to-equity ratio, evaluate long-term financial stability․ These metrics help stakeholders determine a company’s ability to meet obligations and sustain operations, ensuring informed decisions about investments and creditworthiness․
3․3 Analyzing Cash Flow Management
The cash flow statement provides insights into a company’s cash inflows and outflows, essential for evaluating liquidity and financial stability․ It details cash movements across operating, investing, and financing activities, helping stakeholders assess the company’s ability to meet obligations and generate future cash flows․ This analysis is vital for decision-making, ensuring sustainable operations and growth․
Importance of Reliable and Relevant Accounting Information
Reliable and relevant accounting information is essential for accurate decision-making, ensuring transparency and accountability․ It provides a clear understanding of financial performance, supporting informed choices and stakeholders’ trust․
4․1 Qualitative Characteristics of Financial Information
Financial information must possess qualitative characteristics such as relevance, reliability, comparability, and consistency․ Relevance ensures data is timely and useful for decision-making, while reliability guarantees accuracy and neutrality․ Comparability allows stakeholders to evaluate performance across periods or companies, and consistency ensures uniformity in accounting practices, enhancing transparency and trust in financial reporting․
4․2 Impact of Reliable Information on Business Decisions
Reliable financial information fosters informed decision-making by providing accurate and timely data․ It enhances credibility and trust, enabling stakeholders to assess risks and opportunities effectively․ With reliable data, businesses can optimize resource allocation, improve profitability, and maintain long-term sustainability, ensuring alignment with strategic goals and stakeholder expectations․

Users of Financial Accounting Information
Financial accounting information serves both internal and external users, aiding management in operational decisions and external stakeholders like investors and creditors in assessing financial health and risks․
5․1 Internal Users: Management and Employees
Management and employees utilize financial accounting information to monitor performance, allocate resources, and plan future operations․ Managers rely on financial data to evaluate efficiency, set budgets, and make strategic decisions․ Employees may use this information to assess company stability and align their goals with organizational objectives, fostering a data-driven work environment․
5․2 External Users: Investors, Creditors, and Regulators
Investors assess financial statements to evaluate profitability and risks, guiding investment decisions․ Creditors use this information to determine creditworthiness and loan terms․ Regulators ensure compliance with accounting standards, maintaining market integrity․ Transparent and reliable financial data are critical for these stakeholders to make informed decisions, fostering trust and stability in financial markets and regulatory environments․
Management Accounting and Its Role in Decision-Making
Management accounting provides financial and non-financial information to support internal decisions․ It aids in planning, controlling, and evaluating performance, enabling managers to allocate resources effectively and achieve organizational goals․
6․1 Budgeting and Forecasting Techniques
Budgeting and forecasting are essential tools in management accounting, enabling organizations to plan and control resources effectively․ These techniques involve financial modeling and trend analysis to predict future outcomes, ensuring alignment with strategic goals; By establishing benchmarks and monitoring performance, businesses can make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and adapt to changing market conditions efficiently․
6․2 Performance Evaluation and Cost Management
Performance evaluation and cost management are critical for assessing organizational efficiency and profitability․ Financial accounting information helps identify cost drivers, optimize resource utilization, and measure performance against targets․ By analyzing variances and trends, businesses can implement corrective actions, enhance profitability, and achieve long-term sustainability through data-driven decision-making and effective cost control strategies․
Financial Statement Analysis Techniques
Financial statement analysis techniques, such as ratio, trend, and comparative analysis, convert data into actionable insights for informed decision-making, enhancing profitability and strategic planning․
7․1 Ratio Analysis: Liquidity, Profitability, and Efficiency
Ratio analysis evaluates financial performance through metrics like liquidity (current ratio), profitability (ROE), and efficiency (asset turnover)․ These ratios provide insights into a company’s ability to meet obligations, generate profits, and use resources effectively, aiding stakeholders in making informed decisions․
7․2 Trend Analysis: Identifying Patterns Over Time
Trend analysis examines historical financial data to identify patterns and changes over time, helping to forecast future performance․ By tracking metrics like revenue growth, expense trends, and profit margins, businesses can detect strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities, enabling better strategic decisions and long-term planning․
7․3 Comparative Analysis: Benchmarking Against Industry Standards
Comparative analysis involves benchmarking a company’s performance against industry standards or competitors․ This provides insights into relative strengths and weaknesses․ By comparing metrics like profitability ratios and cost structures, businesses can identify areas for improvement, optimize resources, and align strategies with industry best practices, enhancing decision-making and competitive positioning․
Impact of Accounting Regulations on Financial Reporting
Accounting regulations like IFRS and GAAP ensure transparency and consistency in financial reporting․ Compliance with these standards enhances the reliability of financial data, aiding informed decision-making․
8․1 Overview of IFRS and GAAP
IFRS and GAAP are global accounting standards that ensure consistency and transparency in financial reporting․ IFRS, developed by the IASB, is widely adopted internationally, while GAAP, primarily used in the U․S․, provides detailed guidelines for financial statement preparation․ Both frameworks aim to enhance comparability and reliability of financial information, aiding stakeholders in making informed decisions․
8․2 Compliance and Its Effects on Decision-Making
Compliance with accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP ensures accurate and reliable financial reporting, which directly impacts decision-making․ Adherence to these frameworks enhances credibility, allowing stakeholders to make informed choices based on consistent and comparable data․ Non-compliance risks penalties and erodes trust, potentially leading to suboptimal decisions and financial instability for businesses․

Challenges in Using Financial Accounting Information
Financial accounting information faces challenges like limitations of historical data and potential biases in reporting․ These issues can hinder decision-making, requiring users to seek additional, reliable data for accurate insights․
9․1 Limitations of Historical Financial Data
Historical financial data provides insights into past performance but lacks predictive power for future outcomes․ It does not account for emerging trends, market shifts, or unforeseen events, potentially misleading decision-makers․ Relying solely on historical information may result in outdated strategies, emphasizing the need for complementary forward-looking analyses to ensure comprehensive decision-making processes․ This limitation underscores the importance of integrating additional data sources․
9․2 Potential Biases in Financial Reporting
Financial reporting can be influenced by biases, such as management’s incentives to present a favorable outlook, affecting decision-making․ Accounting practices and estimates may introduce subjectivity, leading to discrepancies in reported figures․ These biases can distort the true financial health of an organization, making it essential for users to critically analyze and interpret the information with awareness of potential manipulations or omissions․
The Role of Technology in Financial Accounting
Technology has transformed financial accounting by automating processes, enhancing accuracy, and enabling real-time data analysis․ Tools like ERP systems and AI-driven platforms optimize decision-making, ensuring efficient financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards․ Digitization streamlines operations, reducing errors and improving accessibility of financial information for stakeholders․
10․1 Automation and Digitization of Financial Processes
Automation and digitization have revolutionized financial processes, reducing manual effort and enhancing efficiency․ By implementing tools like ERP systems and AI, companies achieve faster and more accurate financial reporting․ Digitization ensures seamless integration of data, enabling real-time analysis and informed decision-making․ These advancements also improve compliance with accounting standards, reducing errors and increasing transparency in financial operations․
10․2 Big Data and Its Impact on Decision-Making
Big Data significantly enhances decision-making by providing vast amounts of detailed financial information․ Advanced analytics extract insights from large datasets, enabling predictive modeling and trend analysis․ This allows businesses to anticipate market changes and make data-driven decisions․ Big Data also supports risk management by identifying potential financial threats, ensuring more informed and strategic choices for sustainable growth and profitability․
Sustainability and Financial Accounting
Sustainability integrates environmental and social factors into financial accounting, enhancing transparency and decision-making while aligning with global goals like SDGs for responsible business practices․
11․1 Integrating Environmental and Social Factors
Integrating environmental and social factors into financial accounting enhances transparency and decision-making by providing a holistic view of a company’s performance․ This approach ensures that sustainability initiatives are aligned with financial goals, enabling stakeholders to assess the firm’s impact on the environment and society․ By incorporating these elements, businesses can make informed decisions that balance economic success with social responsibility and environmental stewardship․
11․2 Reporting on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Financial accounting plays a crucial role in tracking and reporting progress toward Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)․ By integrating SDG-related metrics, companies ensure transparency and accountability in their sustainability efforts․ This reporting framework helps stakeholders assess contributions to global challenges, fostering informed decision-making and aligning financial performance with societal and environmental impact․ It supports long-term value creation and responsible business practices․
Financial accounting serves as a cornerstone for decision-making, providing reliable insights that empower stakeholders․ It aligns business goals with sustainability, driving long-term value and accountability․
12․1 Summary of Financial Accounting’s Role in Decision-Making
Financial accounting provides a clear picture of a company’s past performance and current financial health, enabling informed decision-making․ It offers insights through financial statements, such as income statements and balance sheets, helping stakeholders assess profitability, liquidity, and solvency․ By ensuring transparency and accountability, financial accounting supports strategic planning and resource allocation, aligning business goals with long-term sustainability and value creation․
12․2 Future Trends in Financial Accounting and Reporting
Future trends in financial accounting emphasize technology integration, such as automation and big data analytics, to enhance decision-making․ Sustainability reporting and integrated reporting are gaining prominence, aligning financial performance with environmental and social goals․ Digital transformation and real-time reporting will streamline processes, improving transparency and stakeholder trust, while adhering to evolving regulatory frameworks and global standards․
